The interaction of a sodium ion and an oxide ion. The electrostatic attraction energy between ions of opposite charge is directly proportional to the charge on each ion (Q 1 and Q 2 in Equation 4.1.1). Thus, more energy is released as the charge on the ions increases (assuming the internuclear distance does not increase substantially).
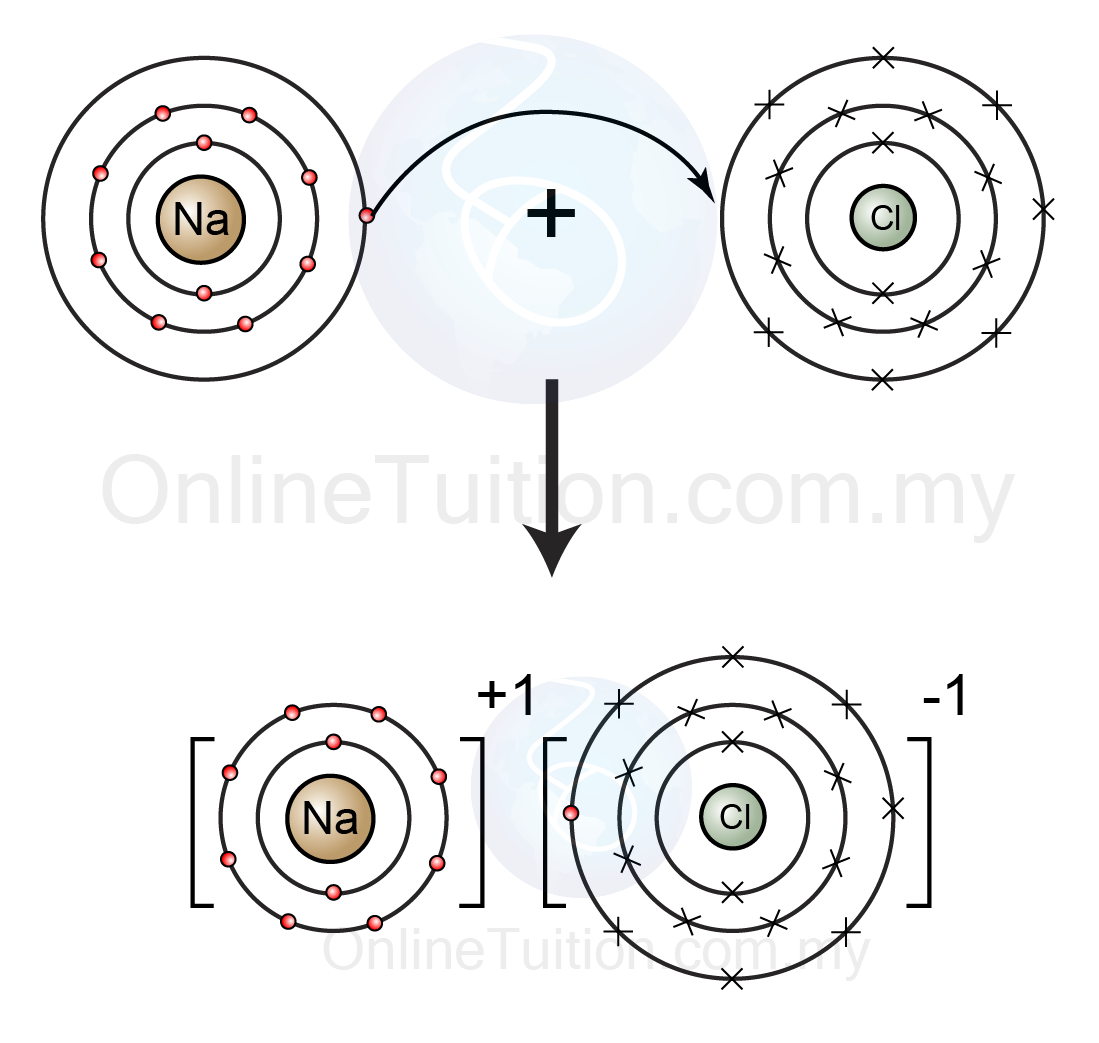
IGCSE Chemistry 2017: 1.40: Draw Dot-and-Cross Diagrams to Show the Formation of Ionic Compounds by Electron Transfer, Limited to Combinations of Elements from Groups 1, 2, 3 and 5, 6, 7
What is the charge of an oxide ion? BUY Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook 1st Edition ISBN: 9781559539418 Author: Angelica Stacy Publisher: MAC HIGHER expand_more Chapter U1 : Alchemy: Matter, Atomic Structure, And Bonding expand_more Section: U1.19 Noble Gas Envy: Ions format_list_bulleted Problem 10E Concept explainers Question
Source Image: spmchemistry.blog.onlinetuition.com.my
Download Image
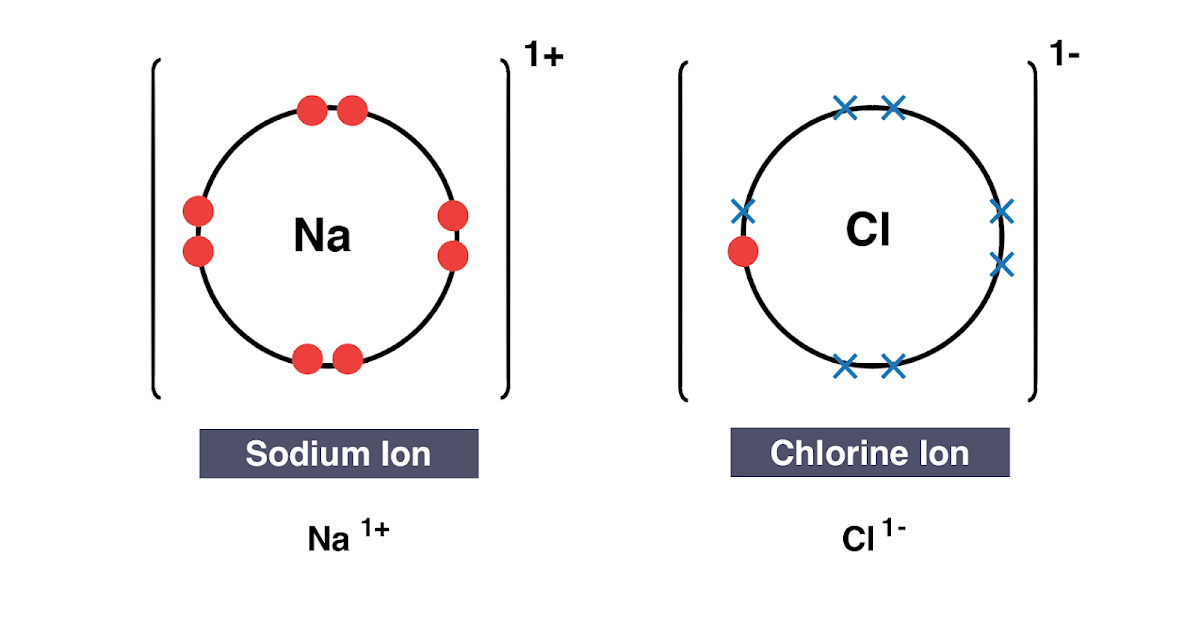
The charge of an ion is indicated by a plus (+) or minus sign (-), which is written to the right of and just above the ion’s chemical symbol. For example, the fluoride ion is represented by the symbol F -, and the sodium ion is represented by the symbol Na +. If the charge is greater than one, a number is used to indicate it.

Source Image: spmchemistry.blog.onlinetuition.com.my
Download Image
Kinetics of Ion Exchange Materials Jul 18, 2022Updated on July 18, 2022 This is a chart of the most common charges for atoms of the chemical elements. You can use this chart to predict whether or not an atom can bond with another atom. The charge on an atom is related to its valence electrons or oxidation state.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
What Is The Charge Of An Oxide Ion
Jul 18, 2022Updated on July 18, 2022 This is a chart of the most common charges for atoms of the chemical elements. You can use this chart to predict whether or not an atom can bond with another atom. The charge on an atom is related to its valence electrons or oxidation state. Mar 23, 2023Ionic charge: When the atom loses or gains one or more electrons, the electric charge is generated (and an ion is formed). This electric charge generated on the ion is known as Ionic charge. When atoms gain electron/s, the negatively charged ion is formed, and when the atoms lose electron/s, the positively charged ion is formed.
Anions Enhance Rare Earth Adsorption at Negatively Charged Surfaces | The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters
Jul 21, 2022An oxide ion, for example, always has a charge of -2. It is impossible for oxygen to form an ion with a -1 charge or a -3 charge. Many metals, on the other hand, form ions that have variable charges. Saying an ion has variable charges means that the same element can form ions with different charges. For example, it is possible for copper to Hydration and Ionic Conduction Mechanisms of Hexagonal Perovskite Derivatives | Chemistry of Materials

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
SOLVED: The total oxide ion charge in a formula unit of MnO is 2–. What is the charge on each manganese ion? Jul 21, 2022An oxide ion, for example, always has a charge of -2. It is impossible for oxygen to form an ion with a -1 charge or a -3 charge. Many metals, on the other hand, form ions that have variable charges. Saying an ion has variable charges means that the same element can form ions with different charges. For example, it is possible for copper to
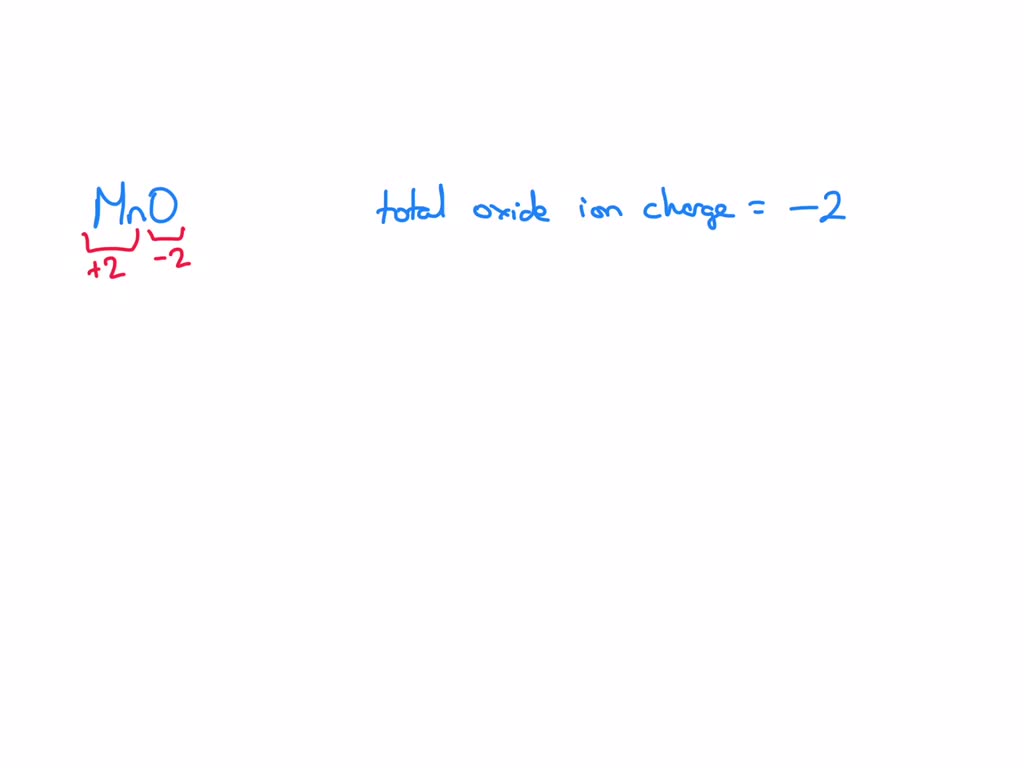
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
IGCSE Chemistry 2017: 1.40: Draw Dot-and-Cross Diagrams to Show the Formation of Ionic Compounds by Electron Transfer, Limited to Combinations of Elements from Groups 1, 2, 3 and 5, 6, 7 The interaction of a sodium ion and an oxide ion. The electrostatic attraction energy between ions of opposite charge is directly proportional to the charge on each ion (Q 1 and Q 2 in Equation 4.1.1). Thus, more energy is released as the charge on the ions increases (assuming the internuclear distance does not increase substantially).
Source Image: igcse-chemistry-2017.blogspot.com
Download Image
Kinetics of Ion Exchange Materials The charge of an ion is indicated by a plus (+) or minus sign (-), which is written to the right of and just above the ion’s chemical symbol. For example, the fluoride ion is represented by the symbol F -, and the sodium ion is represented by the symbol Na +. If the charge is greater than one, a number is used to indicate it.
Source Image: fuelcellstore.com
Download Image
Toward Efficient Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution: Emerging Opportunities with Metallic Pyrochlore Oxides for Electrocatalysts and Conductive Supports | ACS Central Science An oxide ( / ˈɒksaɪd /) is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element [1] in its chemical formula. “Oxide” itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of -2) of oxygen, an O 2- ion with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth’s crust consists of oxides.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Crystal Facet and Architecture Engineering of Metal Oxide Nanonetwork Anodes for High-Performance Potassium Ion Batteries and Hybrid Capacitors | ACS Nano Jul 18, 2022Updated on July 18, 2022 This is a chart of the most common charges for atoms of the chemical elements. You can use this chart to predict whether or not an atom can bond with another atom. The charge on an atom is related to its valence electrons or oxidation state.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
physical chemistry – Charge acquired by sols after their preparation – Chemistry Stack Exchange Mar 23, 2023Ionic charge: When the atom loses or gains one or more electrons, the electric charge is generated (and an ion is formed). This electric charge generated on the ion is known as Ionic charge. When atoms gain electron/s, the negatively charged ion is formed, and when the atoms lose electron/s, the positively charged ion is formed.

Source Image: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Download Image
SOLVED: The total oxide ion charge in a formula unit of MnO is 2–. What is the charge on each manganese ion?
physical chemistry – Charge acquired by sols after their preparation – Chemistry Stack Exchange What is the charge of an oxide ion? BUY Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook 1st Edition ISBN: 9781559539418 Author: Angelica Stacy Publisher: MAC HIGHER expand_more Chapter U1 : Alchemy: Matter, Atomic Structure, And Bonding expand_more Section: U1.19 Noble Gas Envy: Ions format_list_bulleted Problem 10E Concept explainers Question
Kinetics of Ion Exchange Materials Crystal Facet and Architecture Engineering of Metal Oxide Nanonetwork Anodes for High-Performance Potassium Ion Batteries and Hybrid Capacitors | ACS Nano An oxide ( / ˈɒksaɪd /) is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element [1] in its chemical formula. “Oxide” itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of -2) of oxygen, an O 2- ion with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth’s crust consists of oxides.